Copyright © 2025 Motivate Media Group. All rights reserved.
Orkhan Mammadov uses digital art to raise awareness on the importance of cultural heritage
The artist's works uses images of Azerbaijani carpets and other aesthetics from the East
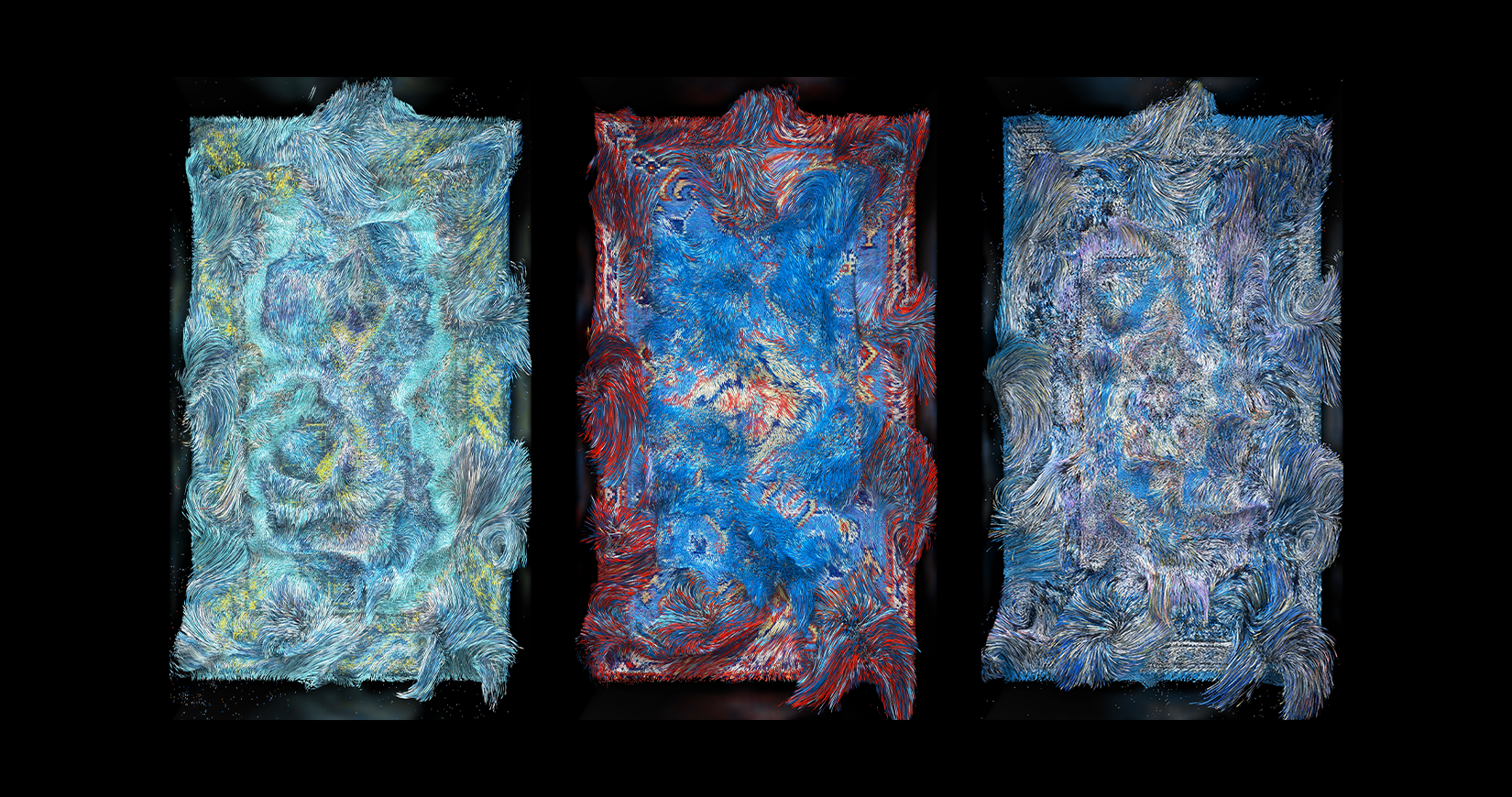
“I am a creative technologist,” begins digital artist Orkhan Mammadov, who has been a pioneer in the digital arts sphere in his native Azerbaijan since 2013 through his first exhibition with Baku-based gallery YARAT. “If we talk conceptually, my paint is data, my brush is algorithms, and the displays are my canvas.” Mammadov’s works are a blend of his Azerbaijani heritage, along with popular aesthetics and references to surrealism, which combine to become Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)-based installations.
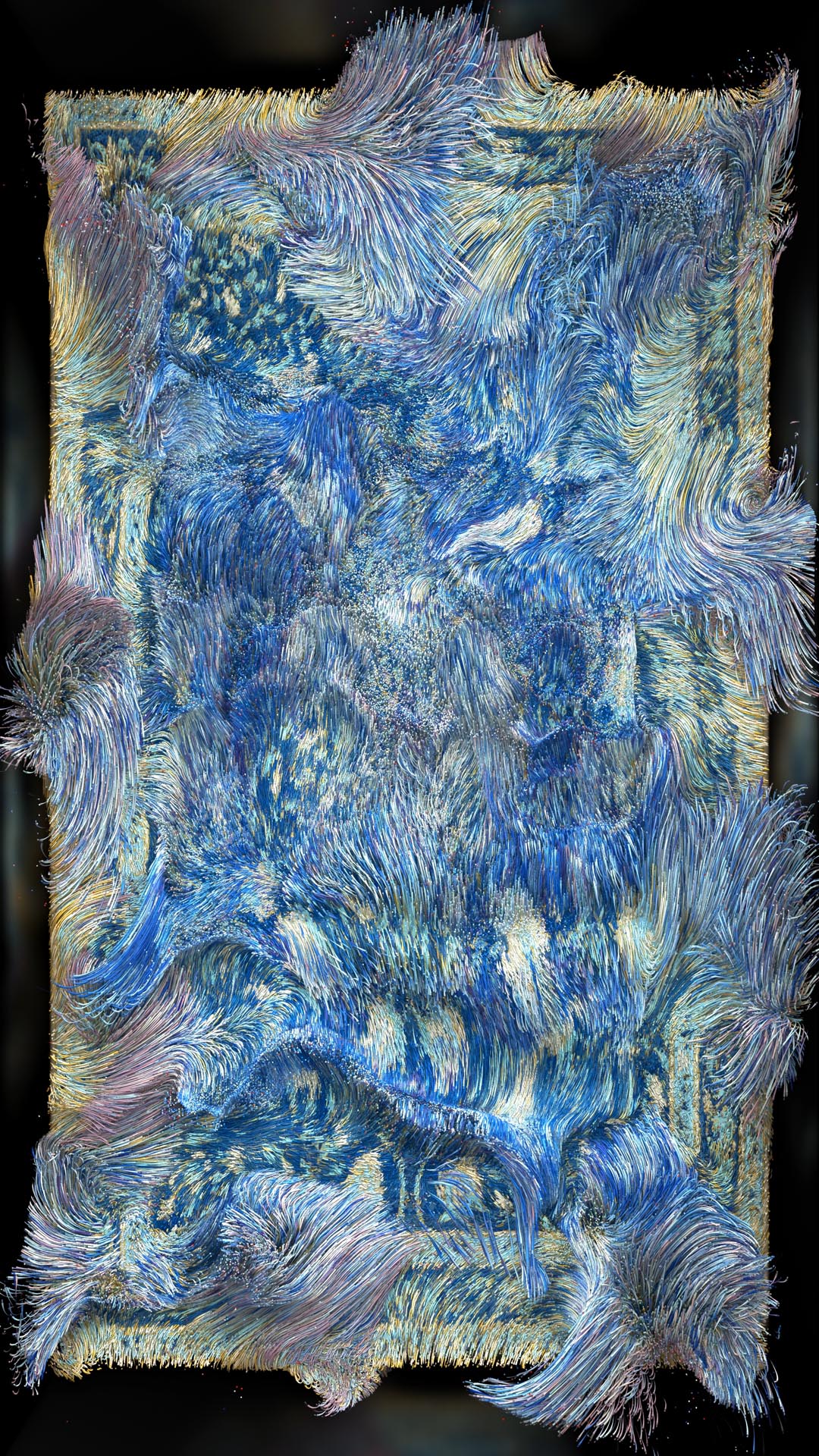

Mammadov’s solo presentation with London-based GAZELL.iO, titled ‘Singularity in Heritage’, was shown during Art Dubai Digital, the fair’s first experience of showcasing a body of digital artworks under the curation of Chris Fussner. Offering a glimpse into the artist’s ongoing research project and autonomous AI art – which was first shown at the Venice Contemporary Biennale in 2019 and the Moscow International Art Biennale – it features a series of video works that are the result of an AI algorithm designed by the artist to understand and find similarities between carpet designs and traditional ornamentation across the Middle East. After processing over 150,000 archival images of carpets, rugs, kilims, miniature paintings and ornamental patterns found across museums and libraries worldwide, a neural network computing system brings together this amalgamation of heritage through a digital lens, enabling the viewer to encounter a visual history of traditional carpet designs – making them the first-ever carpets to be designed in the metaverse.
Historically, carpets, miniature paintings and decorative oriental patterns have played a significant role in forming Azerbaijan’s heritage and aesthetics. And while the Middle East is home to a wide range of carpet traditions, many of them share similarities such as geometric patterns, floral motifs and calligraphic shapes.
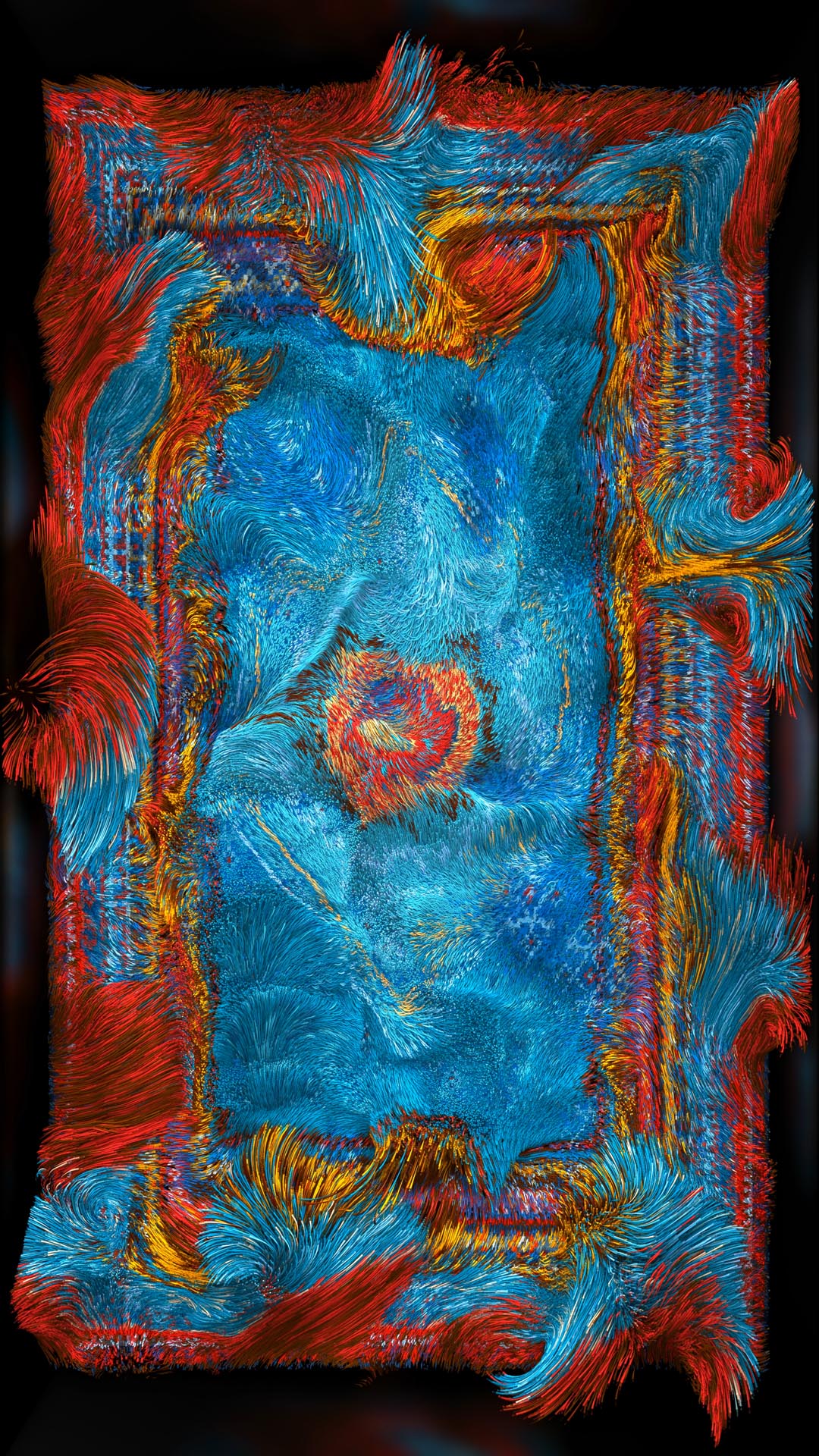
“Perhaps with machine intelligence, we can redefine the concept of repetition,” Mammadov suggests. “The installation’s visual component imitates traditional Azerbaijani patterns. As a result, viewers see how AI builds new alternatives. These alternatives have a synthetic nature that has nothing to do with the history of authentic ornament patterns. AI imitates and fakes a traditional learning process [that is] usually handed down from generation to generation.
“By accessing the data of authentic ornament images, AI becomes an independent master that can invent new ideas to update culture,” he continues. “Besides symbols, AI generates new concepts and meanings. It blurs the boundaries between [what is] real and [what is] fake. These actions further prove cultural development, as non-human intelligence replaces traditional craft tools.”
Mammadov likens his creative process to “painting with data”, and although the crafting process is executed entirely through digital means, tangible heritage is vital to his work. “The main goal that I want to achieve through my art is to remind visitors of the value of cultural heritage,” he concludes.
The Latest
How Eywa’s design execution is both challenging and exceptional
Mihir Sanganee, Chief Strategy Officer and Co-Founder at Designsmith shares the journey behind shaping the interior fitout of this regenerative design project
Design Take: MEI by 4SPACE
Where heritage meets modern design.
The Choreographer of Letters
Taking place at the Bassam Freiha Art Foundation until 25 January 2026, this landmark exhibition features Nja Mahdaoui, one of the most influential figures in Arab modern art
A Home Away from Home
This home, designed by Blush International at the Atlantis The Royal Residences, perfectly balances practicality and beauty
Design Take: China Tang Dubai
Heritage aesthetics redefined through scale, texture, and vision.
Dubai Design Week: A Retrospective
The identity team were actively involved in Dubai Design Week and Downtown Design, capturing collaborations and taking part in key dialogues with the industry. Here’s an overview.
Highlights of Cairo Design Week 2025
Art, architecture, and culture shaped up this year's Cairo Design Week.
A Modern Haven
Sophie Paterson Interiors brings a refined, contemporary sensibility to a family home in Oman, blending soft luxury with subtle nods to local heritage
Past Reveals Future
Maison&Objet Paris returns from 15 to 19 January 2026 under the banner of excellence and savoir-faire
Sensory Design
Designed by Wangan Studio, this avant-garde space, dedicated to care, feels like a contemporary art gallery
Winner’s Panel with IF Hub
identity gathered for a conversation on 'The Art of Design - Curation and Storytelling'.
Building Spaces That Endure
identity hosted a panel in collaboration with GROHE.
















